Abbreviations used in this article:
- NSX Advanced Load Balancer = NSX-ALB
- K8s = Kubernetes (8 letters between the K and s in Kubernetes)
- SSL = Secure Sockets Layer
- AKO = Avi Kubernetes Operator (AVI now a VMware product called NSX Advanced Load Balancer)
In one of my previous posts I wrote about how to install and configure AKO (Avi Kubernetes Operator) to use as Service type LoadBalancer.
This post will try to cover the basics of how to use NSX Advanced LoadBalancer by using AKO to handle our Ingress requests (ingress-controller).
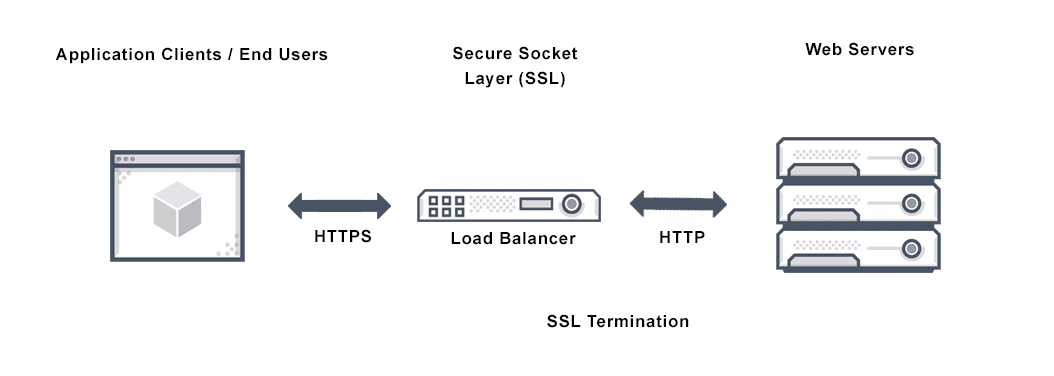
For more information on Ingress in Kubernetes
An API object that manages external access to the services in a cluster, typically HTTP.
Ingress may provide load balancing, SSL termination and name-based virtual hosting.
Ingress Load Balancer Kubernetes Definition #
Within Kubernetes or K8s, a collection of routing rules that control how Kubernetes cluster services are accessed by external users is called ingress. Managing ingress in Kubernetes can take one of several approaches.
An application can be exposed to external users via a Kubernetes ingress resource; a Kubernetes NodePort service which exposes the application on a port across each node; or using an ingress load balancer for Kubernetes that points to a service in your cluster.
An external load balancer routes external traffic to a Kubernetes service in your cluster and is associated with a specific IP address. Its precise implementation is controlled by which service types the cloud provider supports. Kubernetes deployments on bare metal may require custom load balancer implementations.
However, properly supported ingress load balancing for Kubernetes is the simplest, more secure way to route traffic. link
Getting AKO ready #
While this post assumes AKO is already in place and working in your k8s clusters I will get straight to the parts that involve Ingress. If not head over here to read the official docs how to install Avi Kubernetes Operator (AKO). To verify that you AKO is ready to handle Ingress request, type in this and notice the output:
$ kubectl get ingressclasses.networking.k8s.io
NAME CONTROLLER PARAMETERS AGE
avi-lb ako.vmware.com/avi-lb <none> 50d
Default secret for TLS Ingress #
As AKO expects all ingresses with TLS termination to have a key and certificate specified, there is a couple of ways this can be done. We can go with a “pr service”, meaning a dedicated set of keys and certs pr service or a default/common set of keys and certificates that AKO can use if nothing else is specified. To apply the common approach, one common key and certificate for one or more applications we need to add a secret for the AKO. Prepare your router-default.yaml definition file like this (the official docs wants you to put in your cert as is, that does not work so you need to base64 encode both keys and certs and paste in below):
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: router-certs-default
namespace: avi-system
type: kubernetes.io/tls
data:
tls.key: "base64 encoded"
tls.crt: "base64 encoded"
alt.key: "base64 encoded"
alt.crt: "base64 encoded"
To base64 encode your keys and certs this can be done like this:
If you have the keys and certs in a file, from whatever linux terminal type in:
cat cert.pem | base64 -w 0
cat key.pem | base64 -w 0
Then paste into the above yaml accordingly (tls.key:key, tls.crt:crt)
If you have both ECDSA and RSA certs use the alt.key and alt.crt to apply both.
As soon as everything is pasted, apply the yaml file kubectl apply -f router-defaults.yaml
Apply your ingress service #
To create an ingress service you need to define this in yaml. An example below:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: "NameOfIngress-Service"
namespace: "Namespaceofwhereyour-service-resides"
labels:
app: "ifyouwant"
annotations:
ako.vmware.com/enable-tls: "true" #"Indicates to Avi that you want to use TLS"
spec:
ingressClassName: avi-lb #"The default class name for AVI"
rules:
- host: "FQDN"
http:
paths:
- pathType: Prefix
path: /
backend:
service:
name: "which-service-to-point-to"
port:
number: 80
Hostrules and HTTPrules #
As I mentioned earlier, you can also define specific rules pr server such as certificates. Here we can use Hostrules and HTTPrules to further adjust granular settings pr service. One Hostrule example below:
apiVersion: ako.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: HostRule
metadata:
name: name-of-your-rule
namespace: namespace-of-your-service
spec:
virtualhost:
fqdn: must-match-hostname-above # mandatory
fqdnType: Exact
enableVirtualHost: true
tls: # optional
sslKeyCertificate:
name: "name-of-certificate" # This must be already defined in your AVI controller
type: ref
alternateCertificate:
name: "name-of-alternate-cert" # This must be already defined in your AVI controller
type: ref
sslProfile: System-Standard-PFS
termination: edge
To get all features available head over to the official docs site here
Hostrule example from the official docs:
apiVersion: ako.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: HostRule
metadata:
name: my-host-rule
namespace: red
spec:
virtualhost:
fqdn: foo.region1.com # mandatory
fqdnType: Exact
enableVirtualHost: true
tls: # optional
sslKeyCertificate:
name: avi-ssl-key-cert
type: ref
alternateCertificate:
name: avi-ssl-key-cert2
type: ref
sslProfile: avi-ssl-profile
termination: edge
gslb:
fqdn: foo.com
includeAliases: false
httpPolicy:
policySets:
- avi-secure-policy-ref
overwrite: false
datascripts:
- avi-datascript-redirect-app1
wafPolicy: avi-waf-policy
applicationProfile: avi-app-ref
analyticsProfile: avi-analytics-ref
errorPageProfile: avi-errorpage-ref
analyticsPolicy: # optional
fullClientLogs:
enabled: true
throttle: HIGH
logAllHeaders: true
tcpSettings:
listeners:
- port: 8081
- port: 6443
enableSSL: true
loadBalancerIP: 10.10.10.1
aliases: # optional
- bar.com
- baz.com
Httprule example from the official docs:
apiVersion: ako.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: HTTPRule
metadata:
name: my-http-rule
namespace: purple-l7
spec:
fqdn: foo.avi.internal
paths:
- target: /foo
healthMonitors:
- my-health-monitor-1
- my-health-monitor-2
loadBalancerPolicy:
algorithm: LB_ALGORITHM_CONSISTENT_HASH
hash: LB_ALGORITHM_CONSISTENT_HASH_SOURCE_IP_ADDRESS
tls: ## This is a re-encrypt to pool
type: reencrypt # Mandatory [re-encrypt]
sslProfile: avi-ssl-profile
destinationCA: |-
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
[...]
-----END CERTIFICATE-----

